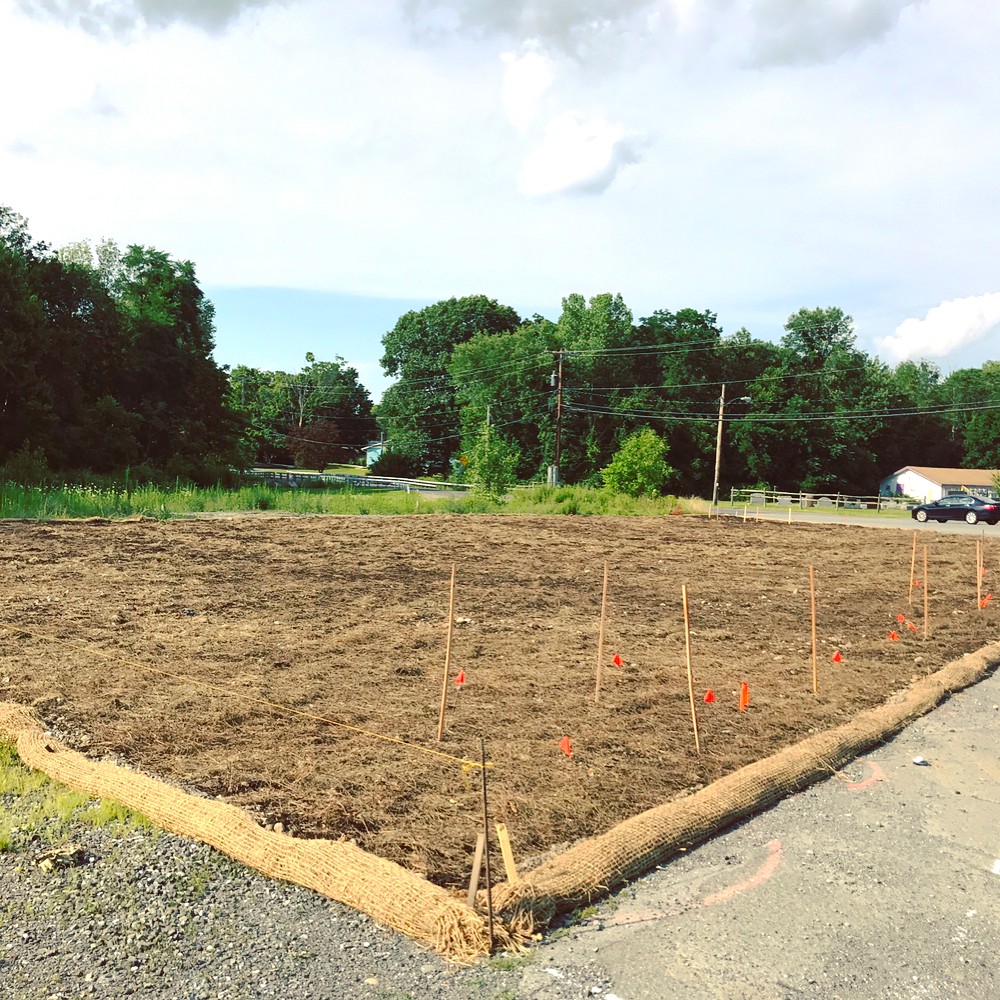
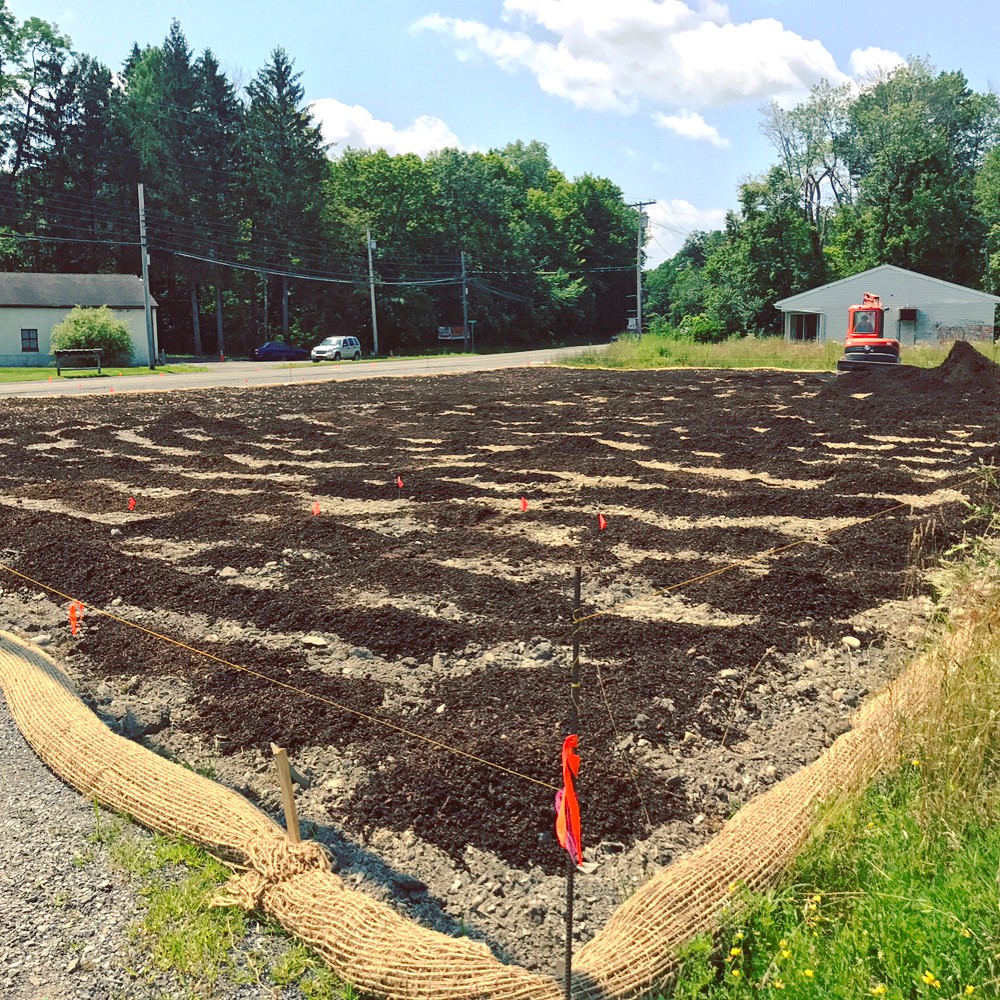
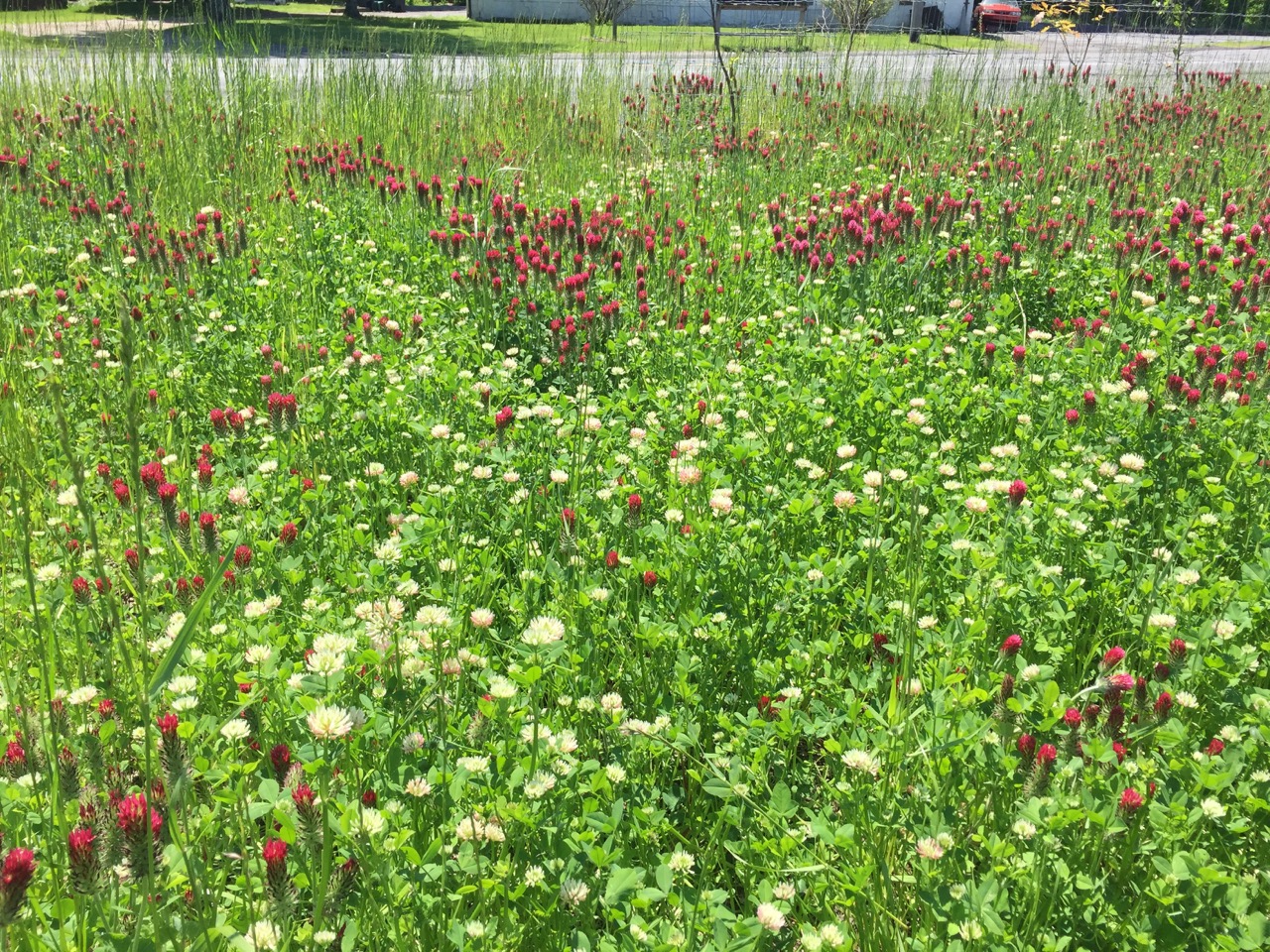
When Hurricane Irene swept through the Northeast in 2011, it caused significant damage to Bushkill Creek, one of the few streams that feed directly into the Ashokan Reservoir in the Catskills. River banks were torn apart and the resulting erosion caused tainted water downstream. One Nature was invited to design a plan for restoring a severely impacted section of Bushkill Creek and the client, Ulster County, agreed to a state-of-the-art bioengineered design to restore a 6-acre section of river and banks. The Bushkill Creek Restoration Project will be completed in the fall of 2016.
Bioengineering—integrating nature into the landscape restoration design—is fast becoming a popular solution for regeneration because the methods are ecologically sound and result in long-lasting revitalization. Designs that are purely engineered, using only non-living materials, are strong at the time of completion but tend to fall apart over time. Bioengineered designs use living material and with time, a bioengineered system gains strength and lasting stability as plant roots take hold and integrate with structural supports. In fact, an engineered design was put in place shortly after Hurricane Irene and subsequently failed.
The first stage of the Bushkill Creek project will be to rebuild and fill in the left bank with soil since much of it was swept away by storm damage and erosion. Trench packing follows—a method of filling small holes in the contour of a stream bank with live branch cuttings and compacted soil to encourage plant growth and stop erosion. Once the soil is shaped, sloped, and trench packed, live stakes and live fascines will be inserted, both of which are instrumental to preventing further river bank erosion in bioengineered design. Live stakes are native, live woody cuttings with the branches trimmed. They soon grow a root mat that stabilizes the earth bed by binding soil particles together. These live stakes, once flourishing, also enhance the beauty of the site and provide a habitat for wildlife. Live fascines are bundles of live brushwood that provide immediate erosion protection. The fascines, which take hold quickly, will be planted parallel to the waterway on both sides of the stream and close to the water’s edge.